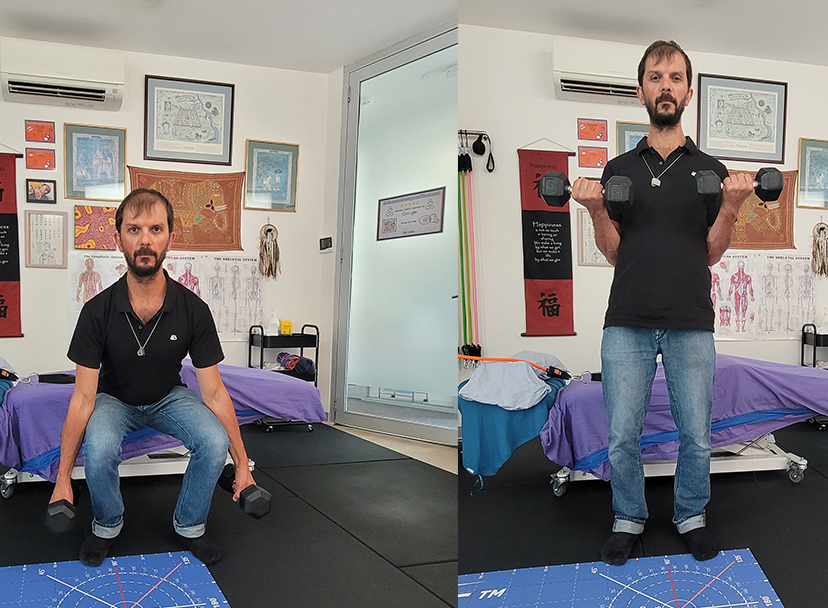
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) disorders are a common source of jaw pain, clicking, and discomfort that can impact anyone at any age. At Melbourne Massage and Treatment in Fitzroy North, I see many clients presenting with TMJ clicking and associated symptoms. One of the key factors behind the painful symptoms is retrodiscal tissue compression, a condition that not only causes joint noises but may also lead to chronic jaw pain. What Causes TMJ Clicking? Let’s start understanding why TMJ clicks. When looking at the TMJ, we can see that between the two bones that make up the joint, there is a disk, called the articular disc, which is made of cartilage and is meant to keep the bones apart (the temporal bone and the mandibular condyle). In a healthy joint, the disc moves smoothly with the jaw during opening and closing. But when the disc is out of alignment, the condyle may snap over it, creating that characteristic “click.” For reference, a condyle is a rounded protuberance at the end of a bone, which in this case, fits into a cavity. The Role of Retrodiscal Tissue Compression in TMJ Clicking and Pain Right behind the disc lies a tissue known as the retrodiscal tissue, which contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. When the disc is displaced anteriorly, the condyle may compress this sensitive area during jaw movements. This compression can lead to: Inflammation Persistent pain Increased joint stiffness Neurovascular irritation This is possible because the tissue, as mentioned earlier, is innervated, whereas the disk is not. Therefore, the disk compression on its own is not going to replicate any pain, as there is no nerve to pick up any stimulus in there. Forward Head Posture Would Not Help. Forward head posture is a common presentation linked to TMJ clicking. Forward head posture is characterised by the head sitting forwards compared to the midline of the body, and is often due to a lack of strength in deeper neck flexor muscles. This presentation can make the TMJ presentation worse because of the excessive load placed on the muscles that surround the TMJ (masseter and temporalis muscles). Other reasons include the misalignment of the teeth, which can make the chewing action more difficult and over time, create strain along the TMJ tissues (muscles, ligaments and tendons), but also referral pain from the cervical joint tension can lead to manifest stress in the jaw and face muscle due to constant pain and discomfort. How Myotherapy Can Help At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, I offer a combination of evidence-based manual techniques and exercise therapy to address the root causes of TMJ dysfunction, aiming not just to manage symptoms but to promote long-term recovery. 1. Joint Mobilisation Gentle mobilisation techniques to the jaw, cervical spine, and upper neck can reduce joint restriction, improve mobility, and relieve the pressure on retrodiscal tissue. Mobilisation helps restore normal disc-condyle mechanics, reducing clicking and improving range of motion. 2. Dry Needling Dry needling of trigger points in the masseter, temporalis, and lateral pterygoid muscles can reduce hypertonicity and relieve pain referred to the jaw and head. Targeting myofascial restrictions can also indirectly reduce stress on the TMJ itself. 3. Targeted Exercise Therapy Specific exercises for jaw control and cervical strength are crucial for maintaining results between sessions. Jaw isometric exercises are ideal for pain management and quick relief. Resistance bend exercises for jaw opening. Relaxation techniques for parafunctional habits like clenching Over time, these exercises can enhance joint stability, reduce overloading, and in some cases improve mild degenerative changes by promoting better joint mechanics and tissue resilience. 4. Deep Tissue Massage Massaging the muscles surrounding TMJ and the cervical muscles can help reduce tension, stimulate the nervous system to relax and give a break from pain and discomfort, while improving mobility. As always, there is not one solution for the common presentation of many. Each individual is different, and the treatment results can be different. But what we can expect is that, if we balance the usage of hands-on treatment and exercises, we can create some real change with some great benefits. TMJ Clicking and Menopause Menopause is a topic I have already spoken about in my blogs. Briefly, we can refer to menopause as the period of 12 months or more of missing menstrual periods in a woman’s life cycle. Before that is called perimenopause, and after that, we talk about post-menopause. This step is achieved when a woman has no more eggs to release, and her menstruation has stopped. While it is not the same journey for each woman and there are many changes that women can go through, a common one is stiffness of ligaments. Again, this is not happening in one day, but is a change that comes with time and is different person to person. This is possible because of the lack of estrogen. Indeed, estrogen, along with controlling many other aspects of the biological life of a woman, is also responsible for the elasticity of the ligament. Put: less estrogen, less elasticity. This can explain why, during this phase, women start experiencing more TMJ pain and potentially TMJ clicking. On the other hand, we have no yet enough evidence to say that Hormonal Replacement Therapy is effective for establishing this presentation (Robinson et al., 2019). FAQ – TMJ Clicking 1. What causes the clicking sound in the TMJ?The clicking occurs when the articular disc in the jaw joint becomes displaced, and the mandibular condyle snaps over it during jaw movement. This is often due to disc misalignment. 2. Why does retrodiscal tissue compression cause TMJ pain?The retrodiscal tissue contains nerves and blood vessels. When compressed due to disc displacement, it can lead to inflammation, pain, and stiffness in the TMJ area. 3. Can TMJ clicking happen without pain?Yes. If the articular disc is displaced but the retrodiscal tissue isn’t compressed or irritated, the joint may click without producing pain. 4. How does forward head posture affect TMJ?Forward head posture strains neck muscles […]
Tag Archives: Menopause
Menopause is a natural phase in every woman’s life, but it comes with a variety of physical, emotional, and mental challenges. As hormone levels shift, particularly estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone, many women experience symptoms like hot flashes, mood swings, sleep disturbances, and weight gain. Fortunately, for managing menopause symptoms, various lifestyle changes can be put in place, such as exercise, a balanced diet, improved sleep hygiene, and stress management techniques. In this blog, we will explore how adopting a healthier lifestyle can significantly improve your menopausal experience. Exercise and Physical Activity For Managing Menopause Symptoms Exercise is again the best recommendation for health improvement that can be offered here. Of course, implementing exercises alone without following any other changes or advice (where needed) is not going to do the trick. But let’s start from here. Exercises can improve overall health and have specific benefits that help ease common issues like weight gain, mood swings, and hot flashes. But not only that. Indeed, exercises, and in particular strength training, are positive stress, which allows the body to regenerate and ensure the slowing down of bone and muscle mass, which is one of the main issues that a woman going through menopause is going to face. Here is a list of exercise routines that you could focus on. But keep in mind that if you really want to choose, I would strongly suggest Strength Training. Aerobic Exercise:Walking, swimming, cycling, or jogging would help in improving circulation, promote heart health, and relieve stress (for the last one, especially if done in open-air environment). Regular aerobic exercise has also been shown to reduce the frequency and intensity of hot flashes. Plus, it aids in weight management, especially during menopause when metabolism slows. Strength Training:Engaging in strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or resistance band workouts, helps preserve muscle mass and improve bone density, which decreases as estrogen levels decline. This is essential for reducing the risk of osteoporosis and maintaining strong bone and muscle mass. Yoga or Pilates:Both yoga and Pilates are great for improving flexibility, balance, and muscle strength while reducing stress and anxiety. These low-impact exercises help maintain your physical health and mental well-being, both of which can be affected by hormonal fluctuations during menopause. Tai Chi or Qigong:These ancient practices involve slow, deliberate movements and deep breathing. They are excellent for enhancing balance, reducing stress, and promoting relaxation—especially helpful for managing mood swings and anxiety. Eating an Anti-Inflammatory Diet A nutrient-rich diet can significantly help in managing menopause symptoms. By incorporating specific foods and avoiding certain triggers, you can reduce inflammation, balance hormones, and support your body’s needs during this transition. Phytoestrogens:Phytoestrogens are plant-based compounds that mimic estrogen in the body and can help alleviate symptoms like hot flashes and night sweats. Foods rich in phytoestrogens include soy products (tofu, tempeh, edamame), flaxseeds, lentils, chickpeas, and whole grains. Calcium and Vitamin D:As estrogen levels decline, the risk of bone loss and osteoporosis increases. To support bone health, incorporate calcium-rich foods such as leafy greens (kale, broccoli, sesame seeds), fortified plant-based milks, and dairy products. Vitamin D is crucial for calcium absorption, so get it from sun exposure or foods like fatty fish (salmon, mackerel) and fortified foods. Vitamin D is cumulative, so during the longer days of the year, ensure to spend some extra time in the sun. But of course, do so during the safest hours and not at UV light pick time. Regarding Vitamin D and Calcium supplements, there is a strong debate about whether they are good or what potential side effects they have, so you’d better talk to your GP about the specifications. Healthy Fats:Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce joint pain and inflammation during menopause. These healthy fats also support heart health, which is increasingly important as estrogen levels drop. Whole Grains and Fibre:Fibre helps stabilise blood sugar levels and improves digestion, which can be helpful as metabolism slows. Incorporate fiber-rich foods like whole grains (brown rice, oats, rye), fruits, vegetables, and legumes to support digestive health and reduce bloating. In the case of beans and grain, ensure that they are soaked when needed to reduce the bloat side effect. Limit Sugary and Processed Foods:Foods high in sugar and processed carbs can cause blood sugar spikes and crashes, leading to irritability and fatigue. This is where having a variety of fresh food is a key component. So yes, no one wants you to overstress about what you eat or not, but, generally speaking, if you have never looked into a balanced anti-inflammatory diet, it is time to do so. Reducing Alcohol and Inflammatory Foods Both alcohol and inflammatory foods can exacerbate menopause symptoms, so limiting or avoiding them can provide significant relief. Limit Alcohol:While alcohol might seem like a way to unwind, it can actually trigger hot flashes, disrupt sleep, and contribute to mood swings. Moderation is key—try limiting your alcohol intake to no more than one drink per day, and if possible, reduce it further to see if it improves your symptoms. Alcohol is a substance that the body does not recognise, and it has quite a hard time breaking it down. Avoid Inflammatory Foods:Highly processed foods, refined sugars, and trans fats can increase inflammation in the body and worsen menopause symptoms like joint pain, fatigue, and mood swings. Instead, focus on anti-inflammatory foods such as berries, leafy greens, fatty fish, and nuts to support your body during this phase. Inflammatory foods are all those that contain Omega-6 fatty acids, which are long-chain fatty acids, that would get collected in your Lymphatic System at first, and attacked by the macrophages (white cells), inciting an inflammatory response. Caffeine:Excessive caffeine can disrupt sleep and worsen hot flashes. If you find that caffeine aggravates your symptoms, consider reducing your intake or cutting back on coffee and other caffeinated beverages, especially in the afternoon or evening. Here is a great podcast from ZOE podcast about […]