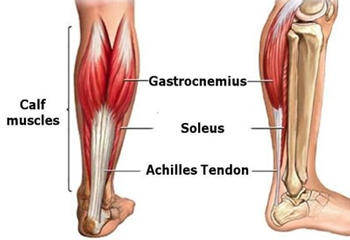
I did stop counting the number of times I hear patients say that their hamstrings are tight, and that’s why they can’t bend forward. And I did stop counting, because this happens so often that it is really hard to find someone who actually knows what tissue is limiting their movement. In fact, most of the time, what is happening is not hamstring tightness, but rather a lack of hip hinging and associated hip mobility, or neural tension (in this case, the sciatic nerve neural tension). What Is Neural Tension? When we discuss neural tension, we refer to the lack of mobility of the nervous system’s connective tissues, so the actual nerve as a fibre or tissue, when it’s put under mechanical stress (like tension, compression, or stretch). Here is an example: When we bend forward, the sciatic nerve (the largest nerve in the body) runs from the lower back (Ventral rami spinal nerve L3-S1), through the buttocks (below the piriformis muscle most of the time), and down the back of the leg (right between the hamstrings muscles). When doing such an action, the nerve needs to glide freely, and if any where along its journey, there is a compression, due to other tissue tightness or inflammation, or even a physical outer pressure (a belt from the pants) it becomes irritated, compressed, or “stuck” ending not moving well. That’s where you may experience a pull on the back of the leg. That is neural tension. More specifically, your symptoms can be: A deep pulling or burning stretch in the back of the thigh or calf. Tingling or numbness (especially if holding the stretch for a longer time) A sensation of “snapping” or “tugging” deep in the leg when stretching Limited range of motion that doesn’t improve with traditional hamstring stretches How Is Neural Tension Different from Muscle Tightness? While neural tension and muscle tightness may feel similar, they are fundamentally different in their causes and treatments. Muscle Tightness Neural Tension Origin Muscle fibres are shortened or tense Nerve or nerve sheath is restricted or irritated Sensation Broad stretch, fatigue, cramping Sharp, burning, electric, or pulling sensation Area Felt Localised to the muscle belly Along a nerve pathway (e.g., back of the leg) Improved by Stretching and massage Nerve gliding/mobilisation, reducing irritation Common in Athletes, post-exercise, poor posture Sciatica, herniated discs, hipo-mobility, and a sedentary lifestyle Now, Let’s Talk About Forward Bending When bending forward with the upper body, aiming to reach the toes or the floor with the hands, we may experience a stretch in the back of the leg. That stretch it may not be only your hamstrings but also the sciatic nerve. When this nerve lacks mobility, as expressed earlier, due to things like disc issues, facet joint irritation, piriformis syndrome, or general irritation, it can feel like your hamstrings or calf or back are tight, even when they’re not. A good way to understand if the feeling of tightness is from your nerve or not is to perform a Slump Test. How to perform a Slump Test? Below is a step-by-step guide on how to perform the slump test: Sit on a chair or table, where both feet are off the ground; Slump your body forward, while looking straight ahead, and your arms are crossing behind your back (which means your spine rounds backward, your shoulder drops forward); Now, start lifting up one leg, while the other one is bent at the knee at 90°; While you lift up the leg, start noticing if you feel any pulling sensation from the lower back going down to the back of the leg or calf (it could be anywhere along the lower back to the feet); If you manage to reach full leg extension, now, start looking down (you may notice tension arising or increasing); If nothing happens yet, then bring your toes (of the leg raised) backwards (ankle dorsiflexion); If, along any step of this process, your pulling sensation increases (more intense) or becomes longer (like from only the back of the leg, it now feels even in the back or in the calf), this is neural tension. Indeed, the tension would feel like a long rope pulled across multiple joints (lumbar, hip, knee) with a burning sensation and maybe some pins and needles. Next, to experiment further with the neural tension, start looking up with the head, go if you can in full cervical extension, and you should feel relief in the back of the leg tension. This last step is proving to you how, by releasing the central nerve (that travels in the central canal of your spine), the neural tension slows down. You are stopping the nerve’s pull from its origin, the brain. Should You Stretch a Nerve? No, not really. Nerves aren’t designed to be stretched like muscles. In fact, if you keep stretching a nerve aggressively, you may end up irritating the nerve and worsening the symptoms. Instead, use nerve gliding or joint mobilisation exercises, which are gentle, rhythmic movements that help the nerve move through its surrounding tissues without overstressing it. And to stay in the loop, let’s look at the sciatic nerve glide: Lying on your back, lift one leg while keeping the knee slightly bent. Slowly extend the knee and flex the foot back toward you, then release. Repeat in small, pain-free ranges. This can help restore nerve mobility without aggravating the nerve. If this is not the case, and you still experience pain and discomfort, then it is probably time to book an appointment (myotherapy) to ensure there is not significant entrapment along the nerve pathway, and see what can be done to relieve that compression. How Myotherapy Can Help with Neural Tension? As a Clinical Myotherapist, I specialised in assisting people with any sort of musculoskeletal issue. Neural Tension is one of those. During a Myotherapy session, we would address, via a detailed clinical history and a series of assessments, what may be the cause of the neural […]
Tag Archives: nerve pain
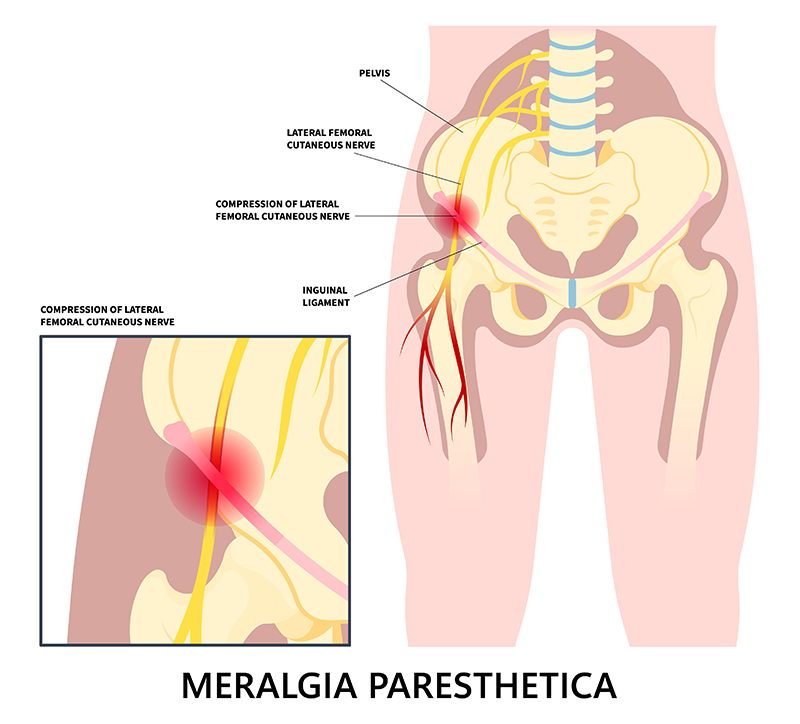
Meralgia Paresthetica is a condition characterized by numbness, tingling, and burning pain in the outer thigh. It occurs when the “lateral femoral cutaneous nerve” (LFCN), which supplies sensation to the skin of the thigh, becomes compressed or irritated. While not life-threatening, it can be uncomfortable and disruptive to daily activities. Now let’s see how Myotherapy treatment can help with this presentation. Causes of Meralgia Paresthetica Meralgia Paresthetica presents with symptoms of lateral thigh weakness and numbness, which are caused by compression or the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. This compression can have typical causes, which include: Tight clothing – Wearing tight jeans, belts, or shapewear can compress the nerve at the hip height. Obesity or weight gain – Excess weight puts pressure on the nerve. Pregnancy – The growing uterus may contribute to nerve compression. Prolonged standing or walking – Excessive movement can irritate the nerve. Injury or trauma – Previous surgeries, injuries, or direct impact to the hip area can damage the nerve. Diabetes – Diabetic neuropathy may increase susceptibility to nerve-related conditions. Inguinal ligament – The LFCN passes right under the inguinal ligament, which may create compression on the nerve itself. All those factors can compress the branch of the femoral nerve, which innervates the lateral portion of the thigh. The origin of the nerve is at the lumbar level L2/L3. Indeed, when a portion of the skin has altered sensation, it is often a peripheral compression that causes the symptoms. Symptoms of Meralgia Paresthetica The symptoms for Meraglia Parestetica often involved one leg only, as it is quiet uncommon to get compression bilaterally. Those symptoms include: Burning, tingling, or numbness in the outer thigh. The skin of the lateral thigh can also become very sensitive and painful to the touch. Sharp or aching pain that worsens with prolonged standing or walking. If the compression is due to organs or the inguinal ligament, movement can aggravate the presentation due to the tightness of the structure during movement. Increased sensitivity to touch in the affected area. Muscle weakness is not a symptom, as this condition affects sensation, not motor function. How can myotherapy treatment help individualise this presentation? As a myotherapist, I specialise in muscular skeletal presentations, and we focus on soft tissues. Through a series of assessments, we can determine whether the compression is peripheral or root nerve compression. Let’s see how. Medical History In the first step, we examine the medical history and physical examination, identifying risk factors and symptoms. Along with the physical examination, we examine the Myotome and Dermatome. Examination On top of active range of motion and another orthopedic test to rule in and out other possible presentations, there are some specific tests which we want to focus on, Myotome and Dermatome. The Myotome are resisted movement, like in this case, hip flexion, knee flexion, knee extension, where it would result in positive findings if we have evident weakness and or back pain. This test would rule in a compression to the spine level. Dermatome, on the other hand, are used to test the connectivity of the cutaneous nerve. So with a sharp and soft object, we will mark some line along the thigh area, looking for loss or confused sensations. This test would rule in a peripheral compression of the nerve. Notice that both presentations can be presented at the same time. Other tests that can be done for this presentation include: Electromyography (EMG) – To rule out other neurological disorders. Imaging tests (MRI, X-ray, or ultrasound) – Identifying structural issues or nerve compression. For those tests, Giovanni would write a referral letter for your GP. Treatment Options for Meralgia Paresthetica As often happens, the treatment options are multiple and must be embraced in groups, not individually. The overall aim of any treatment is to relieve pressure on the nerve and reduce symptoms. Here is a list of treatment options and modalities: Lifestyle Modifications Wear loose-fitting clothing to reduce nerve compression. Weight management to decrease excess pressure on the nerve. Avoid prolonged standing or walking if symptoms worsen. Medical Treatments Pain relievers – NSAIDs (like ibuprofen) or acetaminophen for mild pain relief. Myotherapy treatment – along a series of myotherapy sessions we can reduce symptoms and improve the presentation. Corticosteroid injections – Reduce inflammation and pain. Nerve blocks – In severe cases, numbing the nerve can provide relief. Surgical Options (For Severe Cases) Nerve decompression surgery – Relieves pressure on the nerve. Neurectomy – Removing the affected nerve if pain is persistent. How Myotherapy Can Help At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, during a myotherapy session, after ensuring we are dealing with a Meralgia Paresthetica I may use a series of techniques to help you out with your symptoms. What technique to use is based on your individual presentation,, other cohexsitng presentations, adn also your choice and comfort. Here is a list of modalities used during a Myotherapy session: Muscle Energetic Technique (MET) – Helps reduce tension in the hip, thigh, and lower back muscles that may be contributing to nerve compression. Trigger Point Therapy – Addresses myofascial trigger points that can exacerbate pain and discomfort. Mobility and Strengthening Exercises – Improves mobility and reduces pressure on the nerve. Postural Education – Helps correct movement patterns that may be aggravating symptoms. Joint Mobilization – Enhances circulation and reduces inflammation in affected joints. Dry needling – Using a needle can help reduce pain and muscle ache and increase the neurological connection of those same soft tissues. After the hands-on treatment, we will then look into exercises that can help maintain the change we created. That said, there are other precautions to take in consideration, like: Maintain a healthy weight to prevent excess pressure on the nerve. Choose comfortable clothing that doesn’t constrict the waist or thighs. Incorporate gentle mobility and exercise into your routine. Monitor underlying conditions, such as diabetes, to reduce nerve-related complications. Conclusion Meralgia Paresthetica can be managed effectively with lifestyle changes, medical treatment, and preventive care. Myotherapy can be a valuable complementary […]
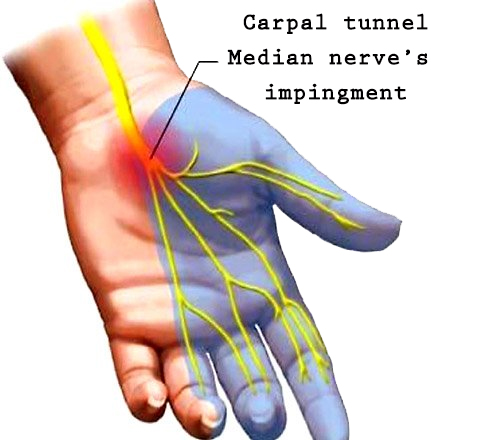
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway in the wrist that opens into the hand. The median nerve runs through the carpal tunnel and gives feeling to the 2nd through the 4th finger (the medial half of it). Carpal tunnel is a condition that affects any gender, and the prevalent of people affected by this condition, are people who do repetitive movements with their hands and arm. Carpal tunnel Symptoms Numbness Pins and needles in the hand Pain, particularly at night Darting pains from the wrist Radiated or referred pain in the arm and shoulder Weakness of the hand The little finger and half of the ring finger are unaffected. Causes of Carpal Tunnel Presentation Occasionally there is no clear cause for Carpal Tunnel. Said so, sometimes there is a combination of factors such as: Arthritis – C.T. is a consequence of inflammation and swelling Pregnancy – During the pregnancy period, given the increase of hormones, the body tends to retain more fluid, which can compress the median nerve and replicate CT symptoms. Genetics – some people can have smaller carpal tunnel Overuse injury – as previously mentioned, repetitive movement and overload of the wrist can lead to CT syndrome Treatment options Along with different treatment options, massage is the first non-invasive approach someone can try for carpal tunnel. As soon as the symptoms show up, it would be wise to go and see a massage therapist. Techniques such as Remedial Massage, Myotherapy can easily address the problem and alleviate the pain. Depending on the presentation and the cause of the carpobual tunnel, even Applied MLD (manual lymphatic drainage) can be an ideal treatment option. Along the physical therapy, rest is highly recommended, and exercises, as often happen, play the main role. To prevent pain from wrist movement, a splint can help. Other treatment options. Surgery is a standard alternative option for Carpal Tunnel. It is a common intervention and can be done on both hands simultaneously. The patient can choose to go for local or general anaesthesia. Surgery for Carpal Tunnel involves a cut along the palm and the wrist. The surgeon then cuts the ligament to reduce pressure on the underlying median nerve. Once the skin gets stitched back, the ligaments heal themselves, and the new scar would not put so much pressure on the median nerve. Even though the surgery is easy, it can have some complications, like swelling and damage to the median or ulnar nerve. Also, if the ligament was not cut completely, it would still apply pressure on the Median Nerve, and a second surgery would be needed.