As previously spoken in another blog post, sitting on the floor and working at the pc would be a better anatomical position than sitting on a chair. Why does sitting on the floor work better than sitting on a chair? Sitting on a chair is uncomfortable, especially in the long term. As a massage therapist, most of my clients are people who have cervical pain or suffer from headaches. Sitting at a desk for hours does more damage than you may realise. So, let’s start with the lower body portion. Staying seated on a chair does direct pressure on the thigh, and by doing so, muscles like the hamstring and gluteus muscles get compressed. By compressing this group of muscles, they get weak and stop functioning as they should. In addition, direct pressure is also applied to the sciatica nerve, the main nerve of the lower body portion. The piriformis often compresses the Sciatica nerve. This muscle runs beneath the Gluteus Max and connects the medial portion of the sacrum to the greater trochanter of the femur. So, the deactivation of those muscles would then manifest itself when we try to walk or, in any case, extend the leg. As the “firing pattern” blog post shows, the hamstring and gluteus max muscles are crucial in leg extension and help prevent lower back pain. This is what happens to the muscle part of the lower body portion. But this is not the only issue the body faces with so many hours sitting on a chair. There is more. So sitting on a chair does limit the body’s movement. The decline of the body’s movement creates a cascade of side effects, including mobility reduction in joints like the Hip, Ankle, Feet, and Thoracic. As all those joints don’t move, there is also a diminish in the proprioception body/brain. Another issue is the compensation of the stability joint over the mobility joint. Indeed, when a mobility joint gets stiff, the stability joint above and below would try to compensate. What’s a common finding pain-wise with sitting on a chair for long hours? The prevalent finding is a sore neck. The sore neck happens as the thoracic stuff up. Indeed the lower cervical portion of the vertebrae, which are stability joints, try to compensate for the thoracic stiffness and, in the long term, would cause neck pain, shoulder pain and headaches. Sitting on the floor can improve mobility. Sitting on the floor can help improve your mobility by allowing you to move your body in many different ways without the need to stand up. That movements are what your body needs as mobility exercises. That movement is your body’s way of improving its posture. Indeed, movement is a crucial component in pain prevention. And this doesn’t happen on a chair. How to switch habits? As for all the habit changes, this has to be gradual and not radical. So, start sitting on the floor for 1 hour a day. Give yourself the time to adapt to the change. Slowly you can incorporate more hours, but not in a row. Maybe one hour in the morning and one in the afternoon. Also, incorporate some standing time to sitting on the chair and floor. Implement change, too, within your training. You are doing something new, and your body needs to adapt. As shown in this clip, start, start implementing a habit of sitting on the floor by doing step-by-step movements: Step 1: Move one leg forward, and bend down the other knee. Step 2: Bring both knees down Step 3: Swing the lower leg to the side (either Lx or Rx) Step 4: Let your body weight go, and sit down Step 5: Now let your lower leg come forward and sit cross-leg. Step 6: Do from step 5 to step 1 in reverse By clicking here, and here you will find the links to a Thai Yoga exercise that can help a lot with improving hip mobility.
Monthly Archives: December 2022
Fibromyalgia is a health condition that causes widespread pain and sensitivity to touch. This type of condition is more common in women than in men, and it is still unknown to science why some people may suffer from Fibromyalgia, even though it is known that stress can play a significant role. On the other hand, genetics can also be the reason why someone can suffer from Fibromyalgia. Fibromyalgia signs and symptoms Symptoms of fibromyalgia may include: headaches sleep disturbances numbness and tingling of the hands and feet muscle and joint stiffness after a period of rest (after sleeping) restlesconditionsndrome Diagnosis of fibromyalgia To be diagnosed with Fibromyalgia, you have to visit your GP first, who may refer you to a specialist. The most widely used clinical criteria for diagnosing fibromyalgia are sourced from the American College of Rheumatology: pain and symptoms over the past week, based on the total of: number of painful areas out of 18 parts of the body The severity of these symptoms: fatigue waking unrefreshed cognitive problems (that can be memory or thought) Plus other general physical symptoms Symptoms lasting at least 3 months, with unchanged Exclusion of other health problems that could reproduce the pain and other symptoms. Treatment and management So, currently, there is no direct cure for fibromyalgia, but there are many treatments that can help manage this condition, like: improving your sleep routine more of a balanced diet relaxation meditation exercise MLD You can also talk to your GP to see what medications can reduce or manage the pain. How MLD can help with Fibromyalgia? Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD) is a gentle, non-invasive manual therapy that aims at boosting the Lymphatic System. Along with the delivery of MLD, the therapist would gently stretch your skin and let the skin recoil, with a pain-free touch. This constant repetitive skin stimulation has a positive impact on the parasympathetic nervous system, which is the portion of the nervous system responsible for what we call “rest and digest” mode. Other benefits delivered from MLD are: Oedema reduction Deep relaxation Inflammation reduction Body’s fluid stimulation Skin health improvement Chronic pain management
Patellar tracking disorder is a condition that occurs when the patella, also known as the kneecap, moves out of its original place when the leg straightens or bends. What causes Patella Tracking Disorder? In most cases, the kneecap shifts towards the outside of your leg, called “Lateral Patella tracking”. Occasionally in some cases, it may shift toward the medial side too. Why this shift happens due to the force applied to the kneecap itself. It was said that the knee joint is a hinge joint, which connects the tibia and fibula of your leg with the femur. The kneecap is held in its natural position by ligaments on the medial and lateral sides and by tendons on the top side. Below the patella is a cartilage layer that helps the patella glide along the femur’s groove. When the cartilage below the patella does wear out, it can create pain and discomfort in the knee. The misalignment of the patella results from tendons, muscles or ligaments that are either too tight or too loose. Lateral patella tracking VS Medial patella Tracking In the case of Lateral Patella Tracking, the Vastus Lateralist is over-developed compared to the Vastus Medialis or the IT Band (Iliotibial Band) pulling too much. Vastus L. can overtake Vastus M’s strengthening due to the muscle size. Indeed the V.L. is visibly bigger than the V. M. On the other hand, tension along Gluteus Max and or tensions in the TFL can play a role in the pulling of the IT band. Are you in Pain, and you suspect to have a Patella Tracking disorder? Get in touch with Giovanni now. [contact-form][contact-field label=”Name” type=”name” required=”true” /][contact-field label=”Email” type=”email” required=”true” /][contact-field label=”Website” type=”url” /][contact-field label=”Message” type=”textarea” /][/contact-form] Risk factors for Patella Tracking Disorder Here is a list of reasons that can lead to Patella Tracking Disorder: Footwear Running Weakness in the quads muscle Unbalance of muscle between the inner and outer regions of your tight Sports that require excessive knee bending, jumping or squatting Improper form or techniques while working out or during sports activities Overweight Genetics (structural reasons) Incidents or trauma to the knees Malformation within the femur bond Damaged cartilage Symptoms Pain is the most symptom of Patella tracking disorder. The pain caused by this condition can occur during regular activity such as standing up, walking and or sitting down. Any knee movement can recreate the pain. In the case of arthritis, the pain can be more intense, and swelling is present at the knee joint. Treatment Options At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, the services available for Patella tracking are multiple. Depending on the severity of the condition, Myotherapy treatment and or MLD are the most recommended. Thanks to Dry Needling and/or Joint Mobilisation therapy, Myotherapy treatment can help rebalance the muscle forces surrounding the knee cap. On the other hand, MLD can help in reducing the inflammation and the swelling present eventually on the knee joint. What then Giovanni would look in, too, is also the mobility of ankles and hips. The correct mobility of these two joints would ensure that the knee is not compensating for the poor joint quality of movement, which can be part of why the patella tracking disorder is in the first place.
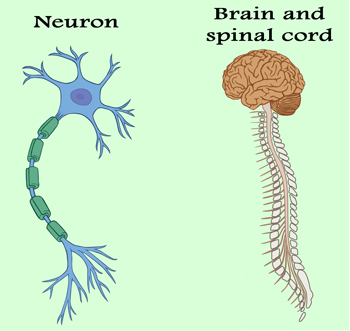
The Nervous System (NS) controls the voluntary and automatic functions of the body. It is made up of: brain spinal cord nerves Subdivision of the Nervous System The nervous system, initially, can be divided into the Central Nervous system (CNS), which is made of the Brain and Spinal Cord and the Perhiperic Nervous System (PNS), which consists of nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body. In more detail, the PNS can be divided into Sensory Neurons and Motor Neurons, the Motor Neurons can be divided into Somatic Neurons and Autonomic Neurons, and finally, this last is divided into the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems. The function of the Nervous System The nervous system can also be defined by its functionality. For this subdivision, we have three categories: Sensory Affarent function Integrative function Motor Efferent Function The afferent function is characterised by a signal that travels to the brain from the PNS. The integrative part analyses the sensory information, stores some aspects, and makes decisions regarding appropriate behaviours. The Motor does respond to the stimulus by initiating an action. The Nervous System is made of Neurons. Neurons carry messages to and from different parts of the body. To be functional, neurons need three components: Oxygen Stimulation Food Neurons can start within the brain and travel down to the spine or can begin with the peripheric portion of the body and travel to the spine and brain next. Either way, the information can travel in one direction only. For afferent neurons, the direction is from the peripheric body portion to the brain, and the efferent is from the CNS or Brain to the peripheric part. Synapses connect neurons. The Synapse is the space where information is exchanged between two neurons. For a signal to be transmitted along a neuron, a chemical reaction has to happen within the neuron cell. This chemical reaction is better known as Action Potential. Once an Action Potential is started, an electric signal, within the order of mV would be transmitted from the Neuron cell to the opposite end, called Axon Terminal. At The Axon Terminal, the neurotransmitter would be passed and sent to the next neuron, receiving those substances through the receptors on its cell membrane. This is just a simplification of how communication between two neurons happens. In reality, there are variations to this communication methodology, and not always does the communication succeed. The NS is responsible for the following: memory, learning and intelligence movement controls the organs’ functions: – heart beating – breathing – digestion – sweating the senses: – sight – hear – taste – touch – smell The Sympathetic and Para-Sympathetic NS. The Autonomic NS controls the body parts we don’t have to think about it, like breathing, sweating or shivering, indeed the main organs. The SNS controls how we respond to emergencies. It makes our heart beat faster and causes the release of adrenaline. Where the parasympathetic nervous system prepares the body for rest (for example, when we go to sleep). The PSNS and the SNS work together to manage the body’s responses to our changing environment and needs. Massage and Nervous System As massage or manual therapy is a direct stimulus of the body, it plays a role in the response of the NS. What can happen is due to genetic factors, muscle tensions, and bulge disk nerves can get trapped along the way. Using the different testing approaches, such as Myotome and Dermatome, Giovanni can guide you through understanding where the nerve got entrapped or pinched. But this type of work is mainly for conditions where physically the nerve is involved in pour functionality. An example can be when someone has poor strength, on one hand, compared to the other, or when the sensitivity of a patch of skin is not so accurate. MLD and Nervous System Another technique, such as MLD (Manual Lymphatic Drainage), plays a role in the Parasympathetic Nervous System. An MLD treatment is profoundly relaxing, as it calms the nervous system, reduces pain and restores balance. This happens because of the mechanic repetitive movement used during the technique. There for, no pain has to be replicated during the treatment, or the SNS gets activated, as per pain response, and the body goes into “alarm” mode. Physical or mental pathologies can play a crucial role in the functionality of the nervous system, and techniques like MLD or Massage therapy generally can help in reducing symptoms and assisting in overcoming pain and body dysfunctions. Along the mental conditions, we find Anxiety or Depression too. In conclusion, any Massage Therapy or Manual Therapy, including Thai Massage, Remedial Massage, MLD and or Myotherapy, are great tools to release the tension in the body and improve the status of the nervous system. On the other hand, breathing, as per already disgust in the breathing wave blogs (Blog 1, Blog 2) plays a vital role in the well-being of the body, mind and nervous system. Feel stressed and need to release some tension? Book now your next massage at Melbourne Massage and Treatment.