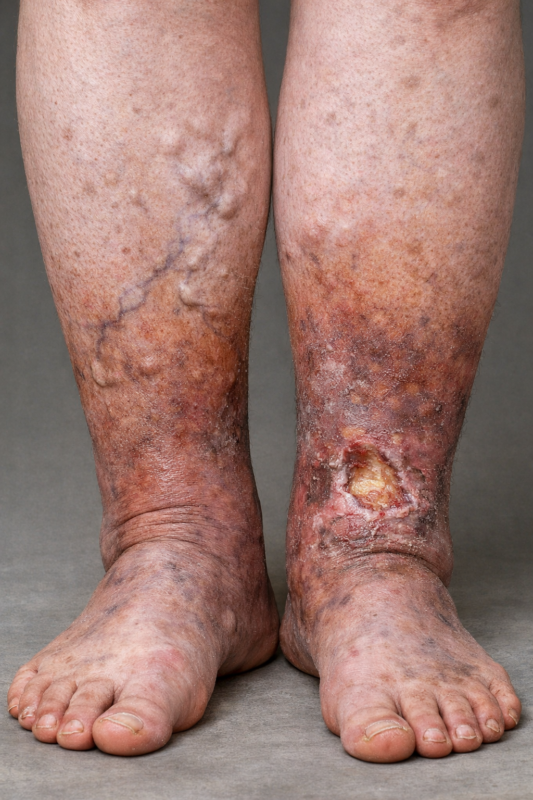
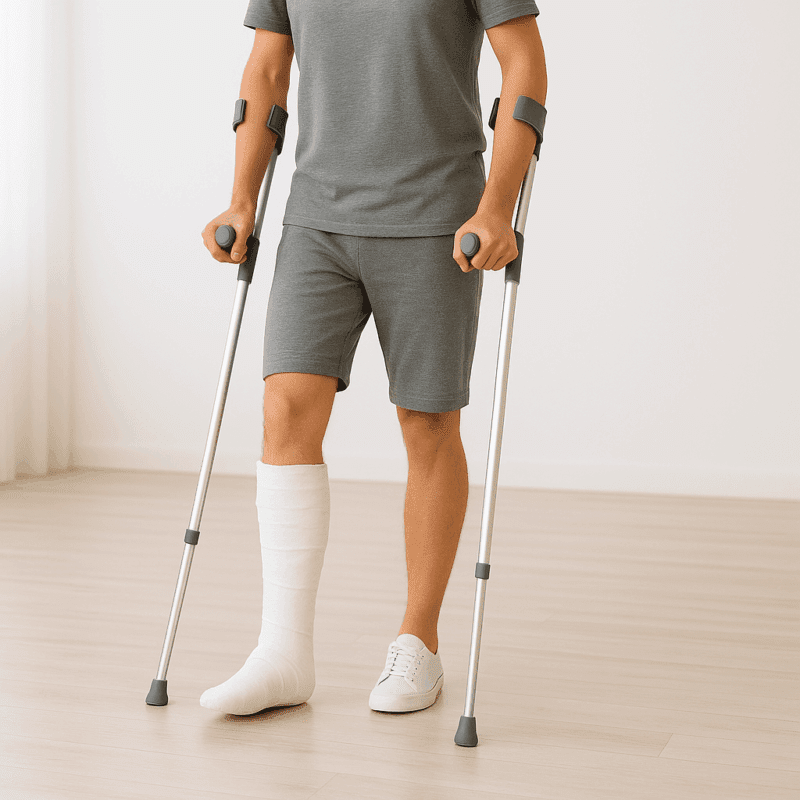
Experiencing a vertebral fracture can be an overwhelming and challenging experience to recover from, but this doesn’t mean there is no safe protocol and successful treatment pathway out there. At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, I am here to assist you in this complex journey, which could be by offering MLD treatment, Myotherapy or Fitness Class. But let’s first understand what fractured vertebrae mean, and what we have to be aware of when working with this type of injury. Spinal Damage vs. No Spinal Damage Let’s start to look into what difference makes to have a spinal fracture where the spinal cord was injured and where it was not. With spinal cord damage, a fracture may injure the spinal cord or nerves, leading to severe symptoms such as numbness, weakness, or paralysis. These cases are medical emergencies requiring hospital care. The rehabilitation process for someone who encounters spinal damage varies based on the severity of the injury. Surgery may be necessary to repair the nerve, but there is also the fact to consider that there may not be a recovery option and life paralysis (quadriplegic or paraplegic) as an outcome. Without spinal cord damage, it is a result of a bone fracture only, without affecting the cord. These are painful but often managed with an initial period of rest and bracing and gradual rehabilitation. At our Fitzroy North clinic, Giovanni carefully assesses your needs and works alongside your medical team to provide safe and effective rehabilitation. Cervical, Thoracic, and Lumbar Vertebrae Your spine has three main regions, and fractures behave differently depending on location: Cervical (neck): Mobile but delicate; fractures here can have severe consequences. Thoracic (mid-back): Stabilised by the rib cage, but injuries here often come from higher-energy impacts. Lumbar (lower back): These vertebrae carry the body’s weight, so fractures here cause significant pain and restricted movement. Based on where the fracture is, the treatment and recovery options and plans differ. Scans for Diagnosis To properly understand the type of fracture and the severity of the fracture itself, scans are essential. Here is a short list of what diagnostic scans are available and which are most commonly used, and why: X-ray: The first step to confirm a fracture. This type of test is good to see the fracture at the bond level; it is quick, but as a downside, it exposes you to radiation. CT scan: Provides detailed 3D imaging to assess the fracture’s stability. The downside of a CT scan is that, as it is based on X-Ray technology, it can still expose you to radiation, and it can take longer to be delivered, and it is essential to be lying down while receiving the scan. MRI scan: Compared to X-Ray technology, MRI scan would not expose you to radiation, and is used to detect any involvement of nerves, discs, or the spinal cord along the fracture, as this type of scan is used for water-based tissue in the body, and not bones. These scans help guide safe rehabilitation, ensuring the right treatment approach from day one. Something else to keep in mind from the result of the scan is that not everything that a scan shows must impact your life. Indeed, a building disk may show in your scan, but that doesn’t mean that that specific pathology is something related to your spine fracture (it may have been there already before), and that doesn’t mean the body would not look after it while you are recovering from the spine injury. Types of Vertebral Fracture Common fracture types include: Compression fracture – vertebra collapses, often linked to osteoporosis (also called a wedging fracture). Burst fracture – bone shatters outward, sometimes threatening the spinal cord. Flexion-distraction fracture – usually from high-speed accidents where the spine bends suddenly. Fracture-dislocation – bone and soft tissues are displaced, often requiring surgery. Avulsion – It is a type of stress fracture, characterised by a small piece of bone pulled away from the main bone by a muscle or ligament (typical along the transverse process). Mechanism of Injury Fractures can occur from: High-energy trauma – car accidents, falls, sports collisions. Low-energy stress – in osteoporosis, even coughing or bending can trigger a fracture. Scheuermann’s disease – in this specific condition, the vertebrae may grow at different heights compared to the sagittal plane. A meticulous clinical history intake can help in figuring out he chance of you suffering from a vertebral fracture. Healing Time and Recovery As per all non-complex bone fractures, most vertebral fractures take 8–12 weeks to heal, even if recovery varies depending on age, bone health, and whether surgery was required. What we know is that nothing can actually boost the healing, but different therapies, active and passive, can help in assisting the healing process, ensuring a positive outcome. What then can be done during the recovery time is: Early phase: Pain management and protection of the fracture. Rehabilitation phase: Gentle guided movement, strengthening, and improving mobility. With myotherapy support, clients can return to safe daily activities while minimising the risk of re-injury. What to Avoid in the Early Stages of a Vertebral Fracture As mentioned earlier, in the early stage of vertebral fracture, it is important to prevent further damage to the spine and wear a corset that helps in stabilising the spine, while the body is starting the calcification of the bone. Even though you may wear a support, you will want to avoid: Heavy lifting, twisting, or bending movements. Prolonged sitting without support. High-impact exercise or activities. Movement is still recommended, as it can still promote fluid movement and relaxation. Therefore, it is possible to go for walks, move your arms, and move your legs even if in a seated position. Manual Lymphatic Drainage Massage in the Early Phase of a Vertebral Fracture At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, I got to offer MLD as a form of treatment for relaxation, which can have a positive impact on pain perception and tension relief from the spine area. MLD is a gentle […]
Tag Archives: bone fracture
Bone fractures are a common injury, but with proper care and rehabilitation, bones can heal and regain strength. Strength exercise is a crucial component of this healing process, aiding in bone regeneration and restoring mobility and function. How can a bone fracture? Bones can fracture when placed under a load or force that they can’t tolerate. The load tolerance is subjective, person to person, and can vary based on the individual medical presentation and clinical history. Age it is only a circumstance that at the current moment in our society is seen as an increase the chance of fracture, but if we learn to age by keeping our feet via strength training, age would not be anylonger a risk component. Indeed, during the aging process, the bone can become weaker if not stimulate to positive stress, such as load active loads. The less load they received, the less the bone would keep regenerating, due to a slower metabolism. Therefor, as explained in other blogs, strength training is a key to longevity and better health. How can bone fractures heal? When a bone fractures, the body initiates a complex healing process involving several stages: Inflammation: Immediately after the fracture, blood clots form, initiating the healing process. Soft Callus Formation: Fibrocartilaginous tissue begins to bridge the fracture gap. Hard Callus Formation: The soft callus is replaced by a hard bony callus made of woven bone. Remodelling: The bone gradually remodels into its original shape and structure. This process can take several weeks to months, depending on factors like age, overall health, previous clinical history, medication intake and the severity of the fracture. Even though there is nothing that can speed up the recovery, as this is a body’s natural process, there are things that can be done to assist the recovery and ensure that the healing happens as smoothly as possible. Exercises are one of those factors that are part of the healing journey, but have to be incorporated under supervision, to ensure not to aggravate the presentation. The Role of Exercise in Bone Regeneration As mentioned above, and in other blog exercises, specifically strengthening exercises are a positive load for the body tissues, including bone, which can help stimulate the regeneration of those tissues. Obviously, different phases of healing require and can accept different types of strength exercises. So yes, you would not start with a single-leg jump on a broken tibia Stimulates Bone Formation: Mechanical stress from exercise promotes osteoblast activity, leading to new bone formation. Enhances Strength and Flexibility: Regular movement prevents joint stiffness and muscle atrophy. Improves Balance and Coordination: Reducing the risk of future falls and fractures. A systematic review by Kuijlaars et al. (2019) highlighted that physical therapy exercises, whether home-based or supervised, significantly improve functional mobility and strength post-fracture. Recommended Exercises for Recovery At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, I offer assistance with bone fracture recovery exercises throughout the Myotherapy and Fitness class treatment plan. What I would focus on, too, when aiming for recovery, would be: Weight-Bearing Exercises: Including walking or gentle jogging (if we are talking about lower limb injury), to stimulate bone growth; Resistance Training: Using bands or light weights to strengthen muscles supporting the bone, or the joint to which the bone is attached. Flexibility and Balance Exercises: Again, using weights and machinery, we aim to strengthen the muscles that control your overall equilibrium and stability to prevent further falls and reduce the risk of injury. Plyometrics which is most often towards the end of a recovery process from anytype of injury, where we focus on motion that are more close to return to daily activity, and we load your tendon as springs, as per can be doing jumping on the spot or repetitive explosive motions with arms. Clinical Evidence Supporting Exercise in Recovery from Bone Fractures Research, as already mentioned in the Kuijlaars et al. (2019) systematic review, shows the benefits of incorporating exercise into fracture rehabilitation, and below we look into more details about what exercises have to offer in terms of recovery: Improved Healing Rates: Patients engaging in structured physical therapy often experience more robust bone healing (Song, 2022). Reduced Complications: Regular movement decreases the risk of complications like deep vein thrombosis or joint stiffness (Ruan et al., 2023). Enhanced Quality of Life: Maintaining physical activity levels improves overall well-being and independence (Mahindru et al., 2023). What to consider when doing exercises post-bone fractures. While exercise is beneficial, it is always important to approach the recovery process with care: Follow Medical Advice: Always adhere to the guidelines provided by healthcare professionals. Avoid Overexertion: Pushing too hard can hinder healing or cause re-injury. Going hard or going home is not how recovery works. Monitor Pain Levels: Some discomfort is normal, but sharp or persistent pain should be addressed immediately. Pain-wise, on a scale of 0 to 10, we usually aim to get you to experience a comfortable discomfort, based on your worst pain experienced as a maximum threshold. Recovery from an injury, including a bone fracture, is a personal journey, and therefore is unique to everyone, in terms of how quickly it can be and what considerations to take into place during the exercise recovery. FAQs – Bone Fractures Recovery and Strength Training 1. How do bones fracture?Bones can fracture when exposed to forces they cannot tolerate. This tolerance varies from person to person, depending on factors like health history, bone density, and physical condition. While age is often seen as a risk factor, it’s more about reduced activity levels. With consistent strength training, the risk of fractures can be lowered significantly, regardless of age. 2. How does a fractured bone heal?Bone healing occurs in four key stages: Inflammation: Blood clots form to protect and initiate healing. Soft Callus Formation: Fibrous tissue bridges the fracture. Hard Callus Formation: New bone begins forming. Remodelling: The bone reshapes to its original form.This process varies in duration based on the severity of the fracture and individual health factors. 3. Can exercise speed […]
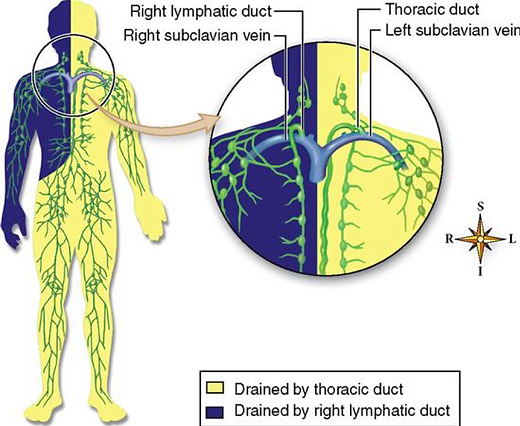
A Watershed is an imaginary line that divides the body and the Lymphatic System into quadrants. Each quadrant has its lymphatic liquid collection canal, and the lower quadrants, as per the two legs, sends the liquid to the cisterna kili, a gland that sits deep behind the belly button that is connected to the upper left duct within the upper left quadrant. Some genetic variation, seeing the thoracic duct connecting to the right lymphatic duct. What does the watershed division look like? The main watersheds are four. A vertical one divides the body into two equal vertical halves. A horizontal one divides the body into the upper and lower body at the inguinal level. Other horizontal watersheds are parallel to each other and are located at: The clavicle line runs through the belly button on top of the iliac crest. In doing so, we have six quadrants: upper, medial, and lower. Other watersheds run vertically within the body. Those are located on the arms and on the upper leg. The importance of watersheds. As we dig more and more within the functionality of the Lymphatic System and MLD as a Lymphatic Drainage technique, we can see that in these specific quadrants, there are bundles of Lymph nodes that get loaded from the lymph vessels connected to them. The watershed division allows the liquid to be directed to a specific body area where lymph nodes are found. Indeed, the lymph nodes are the ones that clean up the lymph fluid, also called obligatory lymph load. When we treat a patient, we have to make sure where we direct the liquid because we want to ensure that the lymph fluid gets sent to the lymph nodes, where it will be processed and then transferred to the lymph/vein duct at the base of the cervical area. This is extremely important when we treat Lymphoedema, where we may bypass the watersheds, where the lymphatic system has been damaged or is missing, to transport the lymphatic fluid from a stagnant area to an active one. How to bypass a watershed To bypass a watershed and transfer the lymphatic fluid from one side of the body to the other side, we have to stimulate the anastomoses, which are the alternative pathways of the lymphatic system. Unless those pathways are stimulated, we can not transfer the fluid side to side along the horizontal or vertical lines. An example would be a person who went through a mastectomy and has a unilateral Lymphoedema. In that case, we need to stimulate the upper anastomosis to transfer the fluid side to side. In the drawing beside, you can notice the upper anterior and posterior anatomoses drawn in thick green lines. The upper watershed and the duct. After the obligatory lymph load reaches the upper watershed (the one running along the clavicle), it gets passed to the venous system. This happens after the obligatory lymph load travels with the trunk collector and passes through the duct. The duct is the last portion of the lymph trunk that connects to the venous system. In conclusion, we want to specify that the lower quadrants (R leg and L leg) and the upper L quadrant drain in the L thoracic duct within the L subclavian vein. Where the R upper quadrant drains into the R duct connected to the R subclavian vein. Below here, is a list of blog posts that talk about conditions where MLD can be beneficial: Bone fracture Sunburn Preeclampsia TMJ Chronic Pain Fibromyalgia Melbourne Massage and Treatment and Lymphatic Drainage Massage At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, Lymphoedema Clinic, I am specialised in Applied MLD and Lymphoedema management. I did train with the Vodder academy for my Lymphatic Drainage practice, and I have a clinical approach to this type of work. If you are in need of manual lymphatic drainage treatment, do not hesitate to book your next appointment now. A 15-minute Online free consultation is also available for those who suffer from Lymphoedema or Lipedema.