Elbow tendinopathy, whether it presents as tennis elbow (lateral elbow pain) or golfer’s elbow (medial elbow pain), is one of the most common overuse injuries in active people, desk workers, and manual labourers. At Melbourne Massage and Treatment in Fitzroy North, I frequently help patients recover from both forms of elbow tendinopathy.
Elbow Tendinopathy: How Does It Manifest?
“Tendinopathy” refers to irritation and degeneration within a tendon due to repeated overload. Elbow Tendinopathy, in both of its forms, tennis or golfer’s elbow, can sound like a sport-related injury, but it has little to do with the sports world. The reason why those presentations carry their name is due to the sport action, which requires that specific muscle group to work to deliver the golfer strike (medial) or tennis strike (lateral).
So what can actually cause an elbow tendinopathy are:
- Sudden increase of tendon load – lifting heavier than usual, at the gym or at work
- Repetitive action – think of that constant mouse or keyboard action in the office environment
- Overstretching of the tendon – Poor office ergonomics can overload the elbow joint and the elbow’s tendons
To be more specific, the office worker presenting with elbow tendinopathy often has repetitive mouse/keyboard use, which is often accompanied by poor ergonomic factors, such as the forearm being in a prolonged pronated position (palm facing down), which places the common extensor digitorum tendon (CEDT) under stretch.
Medial and Lateral Tendinopathy of the Elbow
Let’s look into the difference between the actual Tennis (lateral) and Golfer’s (medial) Elbow.
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
- Pain in the outer elbow
- Irritation of the wrist extensor tendons, especially the Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis (ECRB)
- Familiar with typing, lifting, racquet sports, and DIY tasks
Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)
- Pain in the inner elbow
- Irritation of the wrist flexor tendons
- Related to gripping, pulling, forearm rotation, and throwing
How To Recover From a Tendinopathy?
Despite different pain locations, the rehab approach is almost identical, and while rest provides temporary relief, it does not fix the underlying tendon changes.
The true solution?
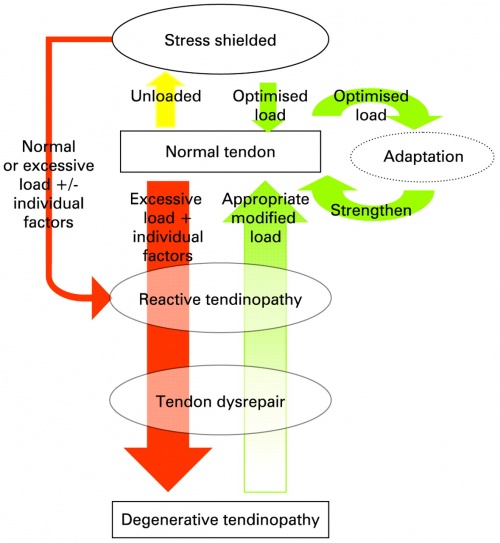
A structured, progressive exercise rehab program that restores tendon strength and resilience.
In fact, as the tendinopathy itself came to be an issue due to an overload of the elbow’s tendon, to settle the pain and discomfort, we have to:
- Reinforce the elbow tendon and muscle so that it can perform better.
- Analyse what overloaded the elbow tendons – we have to understand what can be changed in the loading process, starting from:
- Shoulder stability (looking up in the joint chain – Mobility and Stability)
- The ergonomic of your workload, that is, office or heavy repetitive work (like gardening, for example, or construction).
- Workout program – ensure there is a progressive load in the program that is right for your capacity.
The 3-Phase Exercise Program for Elbow Tendinopathy
Here at Melbourne Massage and Treatment in Fitzroy North, as a clinical myotherapist, I get to see many patients presenting with Elbow Tendinopathy, and the rehab protocol and recovery that I used is detailed below.
Phase 1: Pain Reduction & Tendon Activation (Week 1–3)
In this initial phase, the goal is to calm symptoms without resting the tendon completely. Tendons respond best to gentle, controlled tension, better known as isometric exercises.
Isometric is ideal because:
- Tendons have a low blood supply compared to muscles, so in order to receive the nutrients that allow the healing process to be delivered, they need long and steady engagements.
- A tenodon that is inflamed presents with disorganised collagen fibres, which are not running straight, and no longer form a compact line. And there is a need for a constant load to restore new fibres that can regain the tendon’s functionality.
Wrist Extension Isometric (for Tennis Elbow)
- You will be sitting at a desk with your forearm comfortably supported by the desk, with your hand in a prone position (palm down)
- Slightly extend your wrist against resistance. Pain-free movement (it could be a bend or a lightweight)
- Hold 20 seconds, repeat 10 reps
Wrist Flexion Isometric (for Golfer’s Elbow)
- You will be sitting at a desk with your forearm comfortably supported by the desk, with your hand in a supine position (palm up)
- Deliver a slight wrist flexion against resistance. Again, it has to be a pain-free movement.
- Hold 20 seconds, repeat 10 reps
Time of hold, repetition and pain response are subjective to each individual. That’s where we would stop and focus on each individual clinical history and presentation, and adapt the elbow tendinopathy rehab program to your needs.
Gentle Mobility & Dry Needling
From a point of view of massage for elbow tendinopathy, there are a few techniques that work really well, especially in the early phase of recovery:
- Joint Mobilisation – passive movement applied to the wrist and elbow joint, to improve the range of motion of this joint and disengage the area.
- Dry Needling – The usage of a needle on muscle, to create a micro-inflammation and to drive more attention from the nervous system into the targeted area.
- Deep Tissue Massage – When dry needling is not an option, deep tissue massage can also help in creating this targeted central nervous system response.
Phase 2: Strength & Tendon Remodelling (Week 3–8)
This is the most critical phase, and the one that actually restores tendon health.
Eccentric Wrist Extension (Tennis Elbow Gold Standard)
How to do it:
- Extend the wrist of the affected side with your good hand, while in the affected side, you are holding a lightweight or resistance band.
- Slowly lower the weight with your injured side with a tempo that last 3–5 seconds
- Repeat 12–15 reps, 2–3 sets – this is an endurance setup. Between each set, rest for at least 30 seconds.
Eccentric Wrist Flexion (Golfer’s Elbow Gold Standard)
Same method, but applied in a flexion motion.
- Assist the initial movement of flexion
- Slowly bring the wrist back to the straight position with a 3-5 second tempo.
- Look always at somewhere between 12-15 reps, for endurance performance.
The eccentric exercises are performed to:
- Realign tendon fibres
- Increase load capacity
- Reduce long-term pain.
In fact, we know that it is the eccentric load that places more stress on the actual tissue fibres.
Forearm Rotation (Supination & Pronation)
Using a dumbbell or a twist bar, we are now going to work on the supination or pronation of the forearm. This type of rehab-exercise puts a concentric load on the elbow’s muscles and tendons and aims to reinforce the everyday activity and strengthen the structure.
- Starting by holding the weight in your hand in a neutral position (palm facing medially), rotate the palm up (tennis elbow) or palm down (golfer’s elbow).
- Aim for 10–15 reps each way, use a slow tempo, 3 to 5 seconds, 2 to 3 sets.
- Independent of where your tendinopathy presents, medial or lateral, it is good to do this movement in both directions.
This strengthens deep forearm muscles that stabilise both elbow tendons.
Grip Strength Training
Again, we are looking to strengthen the muscles of your forearm, specifically those that control finger flexion.
- Use a ball or therapy putty
- Squeeze for 3 seconds
- Repeat 15–20 times
Weak grip is not only an indicator of longevity, but it also increases strain on both medial and lateral elbow tendons.
Phase 3: Functional & Sport-Specific Strength (Week 8–12+)
Phases 1 and 2 are for reducing the inflammation, bringing the pain to an ease spot, and giving the muscle and tendon the basic strength needed in the 3rd phase. It is in this phase that we are going to load the muscle and tendon for the daily activity.
Plyometric Wrist Drills
Plyometrics are the exercises that represent the final stage of a rehab program. They tend to replicate the everyday actions we do, and let the tendons work for what they were meant to be: springs.
Plyometrics for elbow tendinopathy would involve actions like:
- Repetitive wrist flexion/extension under resistance load (starting light, increasing load with time and practice)
- Ball catch/release while extending or flexing the wrist
- Tapping on a loaded resistance band with an open hand or a closed fist
Shoulder & Posture Strengthening
As mentioned earlier, elbow tendinopathy could be the result of upper joint chain dysfunction, such as:
- Poor shoulder mobility at the AC joint
- Lack of stability at the scapulo-thoracic joint.
That’s where we will intervene with shoulder assessment and specific exercises to re-establish the proper mobility and strength in the shoulder complex.
Exercises can include:
- Joint Mobilisation
- Rows
- External rotation drills
- Scapular control exercises
- Strength of the upper/middle/lower trap and lat dorsi
- Cuff rot work
Good upper-body mechanics dramatically reduce elbow stress.
Then, of course, based on each presentation, there would be a slight change to the program, based on the progress and the patient’s response.
Why Choose Melbourne Massage and Treatment (Fitzroy North) for Elbow Tendinopathy?
As a clinical Myotherapist, I don’t only focus on the pain spot, but I look for what causes the pain, what can trigger it and maintain it, and I work with you a treatment plan that can help you restore your elbow functionality via:
- Individualised exercise prescription
- Evidence-based loading programs
- Massage for symptom relief
- Strength and movement re-hab
- Ergonomic and technique advice for long-term prevention
I don’t rely solely on passive treatment.
Together will train your tendons to become stronger, healthier, and more resilient.
Book Now You Elbow Tendinopathy Relief


Giovanni La Rocca
Giovanni moved to Melbourne, Australia, from Italy in 2008 and became a citizen in 2017. He started studying massage therapy in 2016, then completed a Bachelor of Health Science in Clinical Myotherapy in August 2024. During those years, he also specialised in Thai Massage and Manual Lymphatic Drainage for presentations like Lipoedema and Lymphoedema. Nowadays, he runs his clinic in Fitzroy North, Melbourne, where he integrates movement therapy into his practice to enhance overall well-being. He also values meditation, having completed several Vipassana courses. Committed to continuous learning, he aims to share his expertise in integrated therapies to help others achieve balance and resilience.