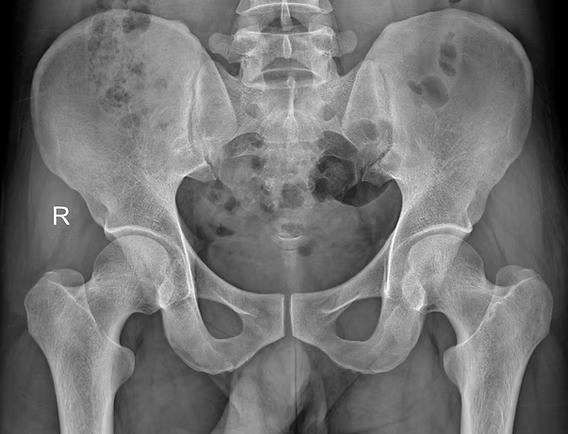
Musculoskeletal pain can be complex, and orthopedic tests and hands-on treatment, sometimes, can be a limited tool to individualise what is happening with the body’s internal structure. Indeed, there are times when a deeper look is required to ensure we are on the right path. This is where body scans imaging comes into play to identify presentations like tendinopathy, bursitis, ligament tear or other underlying conditions. The Role of Body’s Scan in Diagnosing Pathology Body scans include a series of imaging technologies, such as ultrasound, x-ray, MRI, to name a few. Ultrasound is a highly effective imaging tool used to assess soft tissue structures in real-time. Unlike X-rays, which primarily show bone, ultrasound provides detailed images of muscles, tendons, bursae, and ligaments. This makes it an excellent tool for diagnosing conditions such as: Tendinopathy – A chronic condition involving tendon degeneration due to overuse or injury. Bursitis – Inflammation of the bursae, the small fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between tissues. Those tissue types are found along different body joints, like the shoulder and the hip. Ligament Tears – Partial or complete tears of ligaments, often occurring after trauma or excessive stress. Baker’s cyst – is a fluid-filled swelling that forms behind the knee, often resulting from knee joint conditions like arthritis or meniscal tears, causing discomfort and limited mobility. When we are suspicious of one of those presentations, due to positive results obtained by orthopedic test and medical history, including mechanism of injury, we attempt a recovery process, based on the type of injury, symptoms, and other relevant information. Along this recovery process, we may start with isometric exercises. If, with the first 6 weeks, and a series of sessions, 3 to 4 sessions with this time frame, we still don’t see a major recovery, then we may want to get extra investigation ongoing via an ultrasound scan, which can clarify the underlying pathology. It allows us to confirm or rule out certain conditions, ensuring that treatment strategies are aligned with the actual tissue damage (if any is present). On the other hand, based always on the individual case, we could also require X-rays, which are often more helpful in diagnosing conditions related to the bones, such as arthritis or fractures, as they provide a clear view of bone structure and joint spaces. MRI is a scan that is used for Brain imaging, and when the investigation needs higher details, like when looking at the spine or a joint that via ultrasound was not giving any sign of issue. Ultrasound is also comparable to MRI, as it is faster, easier to deliver, and has fewer complications. How can myotherapy treatment help recovery from what a body scans would show? As we already discussed in another blog, Myotherapy is a practice that looks into the well-being of the skeletal muscle structure. To understand what can be done about a painful presentation, we would initially take a detailed clinical history, then look into objective measurements, such as your movement and body presentation. Given the result we can obtain, we would build up a treatment plan which includes: Hands-on Treatment – Techniques such as deep tissue massage, myofascial release, and dry needling can help reduce pain and improve mobility. Exercise Prescription – Strengthening and mobility exercises help restore function and prevent future injuries. Load Management Strategies – Proper guidance on activity levels ensures tissues heal without excessive strain. That management technique would then be combined and adjusted around the scan’s results. Here are a few examples: Bursitis: If a bursitis is confirmed, medications may be given to reduce the inflammation of the bursa, for that, we concentrate on MLD treatment to further reduce the inflammation and exercises to build strength on the structure that needs support. Ligament tear: When talking of ligament tear, the healing time can dilagate to months if not also a year, so we know now why the 6 weeks program may was not as responsive. We will keep focusing on the strength of the muscle that surrounds the specific joint, and use hands-on treatment to boost blood to the area affected. Arthritis: Medication or dietary change may be put in consideration for pain management and inflammatory reduction. Also in this case, MLD can be used to manage the pain response, and exercises for mantain movement in the affected joint/s. When Should You Consider an Ultrasound or other body scans? If you experience ongoing pain, swelling, or restricted movement that is not improving with therapy, an ultrasound or other scan helps identify the cause. This can prevent prolonged discomfort and allow for a more targeted treatment approach. At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, in Fitzroy North, we aim to provide the most effective care possible. If you’re dealing with persistent musculoskeletal pain, book a consultation with Giovanni today. Together, we’ll determine the best action to get you back to optimal function. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Musculoskeletal Pain and Body Scans Imaging 1. What are body scans, and how do they help diagnose musculoskeletal pain?Body scans include imaging technologies such as ultrasound, X-ray, and MRI. These scans help diagnose soft tissue injuries (like tendinopathy, bursitis, and ligament tears) or bone-related conditions (such as fractures or arthritis). They provide a clearer picture of what might be causing pain, inflammation, or restricted movement. 2. Why is ultrasound commonly used in diagnosing soft tissue injuries?Ultrasound is highly effective for real-time imaging of soft tissues like muscles, tendons, bursae, and ligaments. It helps diagnose conditions such as tendinopathy, bursitis, and ligament tears, providing a dynamic view of the area being studied without the need for invasive procedures. 3. When should I consider getting an ultrasound or other scans for my injury?If you’re experiencing persistent pain, swelling, or limited mobility that isn’t improving with initial therapy (such as exercises or hands-on treatment), it might be time to consider an ultrasound or other scans. These can help identify the underlying cause of your symptoms and allow for a more targeted treatment approach. 4. How do orthopedic […]
Tag Archives: tendon
Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome (GTPS) is a common condition that causes persistent lateral hip pain, often making everyday activities like walking, climbing stairs, or even lying on your side difficult. GTPS primarily affects middle-aged individuals, particularly women, and is commonly linked to issues such as gluteal tendinopathy and weakness in the hip stabilizing muscles. At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, our focus is on evidence-based approaches to managing GTPS, and the latest research strongly supports the role of exercise as the first line of treatment for this condition. GTPS Symptoms Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome can present with a series of symptoms that are local to the side of the hip. Here are the most common: Lateral hip pain: Persistent pain on the outer side of the hip, which may extend down the thigh. Pain when lying on the affected side: Discomfort that worsens when lying directly on the hip. Tenderness to touch: Sensitivity around the greater trochanter, which may be painful to press. Pain with movement: Aggravation of pain during walking, climbing stairs, or standing for prolonged periods. Weakness in hip muscles: Reduced strength in the gluteal muscles, leading to instability in movement. Difficulty sitting for long periods: Sitting on hard surfaces can exacerbate discomfort. Mechanism of Injury for GTPS GTPS is primarily associated with tendinopathy of the gluteus medius and/or minimus muscles, with or without accompanying bursitis. As per many tendon injuries, this condition often arises from repetitive stress or overuse, leading to microtrauma and degeneration of these tendons. On the other hand, abnormal hip biomechanics can exacerbate the issue, as compressive forces cause impingement of the gluteal tendons and bursa onto the greater trochanter by the iliotibial band during hip adduction. Contributing factors to GTPS include acute trauma, such as a fall onto the lateral hip, prolonged pressure from lying on one side, and overuse from activities like running or stair climbing. Additionally, conditions like iliotibial band disorders and gluteal muscle weakness can increase the risk of developing GTPS. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for effective management and prevention of GTPS. Evaluation of GTPS Diagnosing GTPS typically involves a combination of clinical examination and medical history assessment. After taking your clinical history, including sports and work activity, I will perform a series of tests to validate the suspicions of GTPS. Those tests include single-leg stance and resisted hip abduction, which we would expect to show weakness in single-leg standing and pain during the abduction movement. Lastly, we would also palpate the area, which is a test that is kept for last because we want to avoid flair the presentation, which may be painful with any other test after that. In some cases, imaging techniques like ultrasound or MRI may be used to rule out other conditions and confirm gluteal tendinopathy or soft tissue abnormalities. I personally do not recommend image testing as the first way to go because the impact of seeing physical damage can also have a negative impact on self-perception, making a recovery harder. At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, our focus is on evidence-based approaches to managing GTPS, and the latest research strongly supports the role of exercise as the first line of treatment for this condition. The difference between GTPS and Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) The difference between GTPS and FAI stands in the hip area involved in the injury. The GTPS is relative to the side of the hip and involves the gluteus medius and minimus tendon and the bursa that separate that tendon from the greater trochanter of the femur. On the other hand, FAI is a presentation that still involves the hip, but it does take place on the anterior portion of the hip, as is characterised by and overgrowth of tissue on the femur head or the hip socket, and it does manifest with hip flexion and external rotation. That’s why it is important to receive an evaluation of the presentation from a professional, in order not to mix the two presentation, or also, in order to evaluate if both presentation are present at the same time, which can also happen. The Role of Exercise in GTPS Treatment A recent systematic review and meta-analysis analyzing multiple randomized controlled trials found that structured exercise provides significant benefits for individuals with GTPS. The findings revealed that: Long-term pain reduction: Exercise can lead to slight but meaningful reductions in hip pain over time. Improved physical function: Patients who engage in targeted exercise programs experience better mobility and overall hip function. Increased likelihood of meaningful recovery: Compared to corticosteroid injections, exercise significantly increases the chances of noticeable improvement in symptoms. One of the most notable takeaways from this research is that exercise has a long-lasting effect, whereas treatments such as corticosteroid injections may provide only short-term relief. Additionally, no serious adverse effects were reported with exercise-based interventions, making it a safe and sustainable approach to managing GTPS. Why Choose Exercise Over Corticosteroid Injections? Corticosteroid injections have often been used for GTPS pain relief, but the research indicates that exercise leads to better long-term outcomes. While injections may offer temporary symptom relief, they do not address the underlying causes of GTPS, such as gluteal muscle weakness or tendon dysfunction. Exercise, on the other hand, strengthens the hip muscles, improves joint stability, and reduces the likelihood of recurring pain. In a previous blog post, I spoke about the key role of Gluteus Medius as a pelvis stabiliser. Effective Exercises for GTPS At Melbourne Massage and Treatment in Fitzroy North clinic, I design individualized exercise programs to help patients with GTPS regain strength and function. Some of the most effective exercises for GTPS include: Isometric exercises: Holding static positions to engage the hip muscles without excessive movement, reducing pain and improving muscle endurance. Strength training: Progressive strengthening of the gluteus medius and minimus muscles to enhance hip stability. Functional movement training: Exercises that mimic daily activities to help improve movement patterns and prevent pain triggers. These exercises can be performed both at home and under professional supervision to ensure […]
When it comes to maintaining a healthy, functional body, it’s easy to overlook the pivotal role of certain muscles in everyday movement and long-term stability. One such muscle is the gluteus medius. At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, located in Fitzroy North, I see many patients who either love running or love to hit the gym but are not aware of the importance of this muscle for their activity. What is the Gluteus Medius? The gluteus medius (GM) is one of the three primary muscles of the gluteal group, located in the upper part of the buttock. Here is a breakdown of its anatomy: Origin: the gluteal surface of the ilium Insertion: lateral surface of the greater trochanter Innervation: dorsal branches of the L4, L5, and S1 Actions: Abduction and medial rotation of the lower limb. It stabilises the pelvis. Thanks to its positioning, the GM plays a vital role in controlling pelvic movement, specifically in the stabilization of the pelvis during various motions like walking, running, or standing on one leg. More Information About Gluteus Medius actions The GM serves several essential functions that directly affect the stability of the hip and lower body: Pelvic Stabilization: One of its primary roles is preventing the pelvis from tilting excessively to one side when you move, especially when you’re walking or running. If the gluteus medius isn’t working properly, the opposite side of your pelvis may dip downward, leading to an imbalance and compensatory movements that strain other parts of the body. Hip Abduction: The gluteus medius helps to move the leg out to the side, away from the body. This movement, known as hip abduction, is crucial for activities that require lateral movement, such as stepping sideways or maintaining balance while performing physical tasks. Internal and External Rotation: The gluteus medius also assists with the rotation of the hip joint. Depending on which fibers are activated, it helps with both internal and external rotation of the thigh. This is essential for maintaining control and precision in movements. Postural Support: The gluteus medius muscle helps keep the pelvis level when you’re standing on one leg. Without proper activation of this muscle, one hip might drop, affecting posture and causing misalignments in the spine and lower back. The Role of the Gluteus Medius in Hip Stability Why is the GM so important for hip stability? Simply put, this muscle acts as the stabilizer of the pelvis. Without a properly functioning gluteus medius, other muscles and joints are forced to compensate for the lack of stability, leading to overuse and strain. For example, improper GM function can result in excessive stress on the knees, lower back, and even the ankles, which can lead to pain, discomfort, and injury. Clinical implications are vast, especially for athletes and individuals who regularly engage in physical activities. Hip instability can result in difficulty performing simple tasks like walking or climbing stairs, and over time, it may contribute to chronic conditions such as hip osteoarthritis. A common painful presentation that we see in athletes but also the everyday patients is Greater Throcanta Pain Syndrome (GTPS), which is characterised by the side hip pain. This presentation results from a GM tendon irritation. Signs of Weak or Dysfunctional Gluteus Medius Here are some common signs that your gluteus medius may need attention: Pain in the hip or lower back: Since this muscle is integral to proper alignment, dysfunction often manifests as discomfort in the hips or lower back. Difficulty balancing on one leg: Struggling with stability when standing on one leg may indicate weak gluteus medius muscles. Shifting or limping while walking: A noticeable shift or limp while walking can point to weakness in the gluteus medius, causing the body to compensate and disrupt your gait. How can Gluteus Medius impact your run? The gluteus medius is crucial for runners as it stabilizes the pelvis, controls hip movement, and ensures proper alignment during running. This muscle prevents excessive pelvic tilting, reduces side-to-side sway, and helps maintain efficient running form, thereby lowering the risk of injuries such as knee pain, IT band syndrome, and lower back discomfort. A weak or dysfunctional gluteus medius can lead to compensatory movements, affecting performance and causing imbalances. How Melbourne Massage and Treatment Can Help At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, as a clinical myotherapist, I focus on treatment designed to address muscle pain and dysfunction through a variety of techniques. One of the key areas of focus is to create a treatment plan that works for your presentation based on your clinical history. Here is a breakdown: 1. Assessment and Diagnosis: I would conducts a thorough assessment to identify if the gluteus medius is underperforming, weak, or compensating due to other musculoskeletal issues. This involves a combination of posture analysis, movement patterns, and targeted strength tests. 2. Myotherapy Treatment Techniques: I will use various techniques, including trigger point therapy, Dry Needling, myofascial release, and deep tissue massage, to release tension in the gluteus medius and surrounding muscles. This helps to restore proper function, reduce pain, and improve mobility. 3. Rehabilitation and Strengthening: After addressing any issues, we will work to develop rehabilitation strategies, including targeted strengthening exercises for the gluteus medius and other muscles that surround the pelvic, lower back and leg area. These exercises aim to restore proper muscle activation and prevent future imbalances. 4. Injury Prevention: In order to prevent further injury, we will set a target of strength that you want to achieve with your sports activity, and we will do our best to hit that target. Be mindful that based on your presentation, the target could extend from a few weeks to several months. The Takeaway The gluteus medius muscle is far more important for hip stability than many people realize. Its role in maintaining pelvic alignment and controlling movement is essential for pain-free mobility, proper posture, and long-term musculoskeletal health. Whether you’re dealing with hip pain, experiencing difficulty with balance, or want to prevent future issues, understanding and caring for […]
A deadlift (conventional deadlift) is a popular exercise that aims to strengthen your posterior chain muscle, including the erector spinae muscle, glutes, and hamstring. It is considered a really top list of important exercises to do, and it can be fun and rewarding, but when the weight you move starts increasing, it can lead to severe injuries if you are not using the right technique. Let’s then look into what we need to do to get a good deadlift by starting to analyse from bottom to top how the body should be placed. Centre of mass and biomechanics in deadlift To start with, let’s talk about the biomechanics and the centre of mass for a deadlift. When doing exercises, biomechanics plays a crucial role in safety and optimal exercise execution, and there is no exception for the deadlift. Furthermore, along with all exercises, the lifting and the descending part, the weight has to be in line with the centre of mass. These two components are strictly interconnected to the other one, which means if I don’t use the right biomechanics, I am not going to have the weight aligned with the centre of mass, or if the weight is not aligned with the centre of mass, I am not using my biomechanics at its full potential. So, what’s the centre of mass in the deadlift? The centre of mass in a deadlift is that imaginary line that runs right from the mid-portion of your feet up right in front of your shins, and as you lift the weight up, it passes right in front of your pelvis. That’s where the bar is going to end once you complete the lifting motion. What happens if I don’t keep the bar along the centre of mass? At any stage, during the lifting or the descending motion, if you move the bar further away from the centre of the mass line, there is a great danger of injury. This is because, as the weight travels away from the centre of mass, there is an increase in momentum, which means that your muscles and ligaments that are working hard to move the weight are suddenly placed under a greater load. What are then the proper biomechanics to observe along a deadlift? Ankle and Knee To execute a good deadlift, we want to ensure we have good ankle dorsiflexion, which is not as important as when we squat, but still, we better ensure it is working right. This would allow a straight forward movement of the knee, which would not need to find its way medially or laterally along the initial bending for when we go to grab the bar. Moving up the chain, as we said, the knee have to point straight ahead, following the toes direction. Hip and lower back Next is the hip. This is an important joint, and here is where we need to make sure that we tilt the pelvis forward (bring the teil bone upwards) and as we hinge the hip, we have to have enough movement in there that the greater trochanter (bone landmark that represents the side of the femur’s head) is posterior to the malleolus (the bone landmark that make the side and medial portion of the ankle). Now, if we managed to have tailbone project far back and up, and hip hinged with a slightly bent knee, our back up to cervical area would be alrady quiet flat. Thoracic and head If we keep going upwards, we get to the upper thoracic area, right between the scapula. Here, we want to keep the scapula protracted and have the rhomboids and serratus anterior muscles active and strong so that the arms can hang down straight towards the bar and sit right next to the knee. Regarding the head, use your eyesight to look down at the floor at 45° in front of you and feel the ears pulling away from the shoulder. That would keep your neck nice and long and place the head in the right position. Arms and hands Arms hang down from the shoulder in a straight line, from the AC Joint down to the wrist. The arm has to feel heavy and prolonged, and the hands must sit right next to the shin. Indeed, your arms must stay as wide as your shoulders. That would ensure that your arms are at 90° with the bar, and from a vertical pool point of view, they can take the maximum load ever. Lastly, regarding the hands, there are different grip types that can be used for the deadlift. What is most important is that the wrist is straight following the armline. For exercise purposes, you can have a regular grip where your thumb is gripping around the bar. For heavier weights, you may want to do a mixed grip, where one hand (the dominant one) has the palm facing forward, and the other hand has the palm facing you. In conclusion, the biomechanics of the deadlift, if used correctly, will allow you to always weight in a safe spot, in line with the centre of mass. Your back has to be flat at all times, and along the exercise execution, you want to grasp air in, engage the core to flat out the lower back and then you can lift off. Benefits of Deadlifting Now, let’s look into the benefits of deadlifting. Full-body workout: Deadlifts engage multiple muscle groups—glutes, hamstrings, quads, lower back, core, traps, and forearms—providing a full-body workout in a single movement. Improved strength: Deadlifts are among the best exercises for building overall strength, especially in the posterior chain (back, glutes, and hamstrings). Better posture: Deadlifts can improve posture and reduce the risk of slouching by strengthening your back and core muscles. Core stability: The movement requires significant core activation, helping to enhance core strength and stability. Increased athletic performance: Deadlifts translate well to other athletic movements, as they improve explosiveness, agility, and endurance. Fat loss: The intensity and demand on […]
In the world of fitness and wellness, stretching has long been hailed as a crucial component of any exercise regimen. But what if we told you that the benefits of traditional stretching might not be as clear-cut as we’ve been led to believe? At Melbourne Massage and Treatment in Fitzroy North, we believe it’s essential to examine the science behind standard practices. Let’s dive into why the traditional notion of stretching might be more myth than fact. The Stretching Paradigm For decades, stretching has been touted as the go-to method for improving flexibility, preventing injury, and enhancing performance. From pre-workout rituals to post-exercise cooldowns, the idea is ingrained in our fitness culture. However, recent research suggests that many of these beliefs may lack substantial scientific backing. Limited Evidence for Injury Prevention One of the primary arguments for stretching is its role in preventing injuries. Yet, numerous studies have indicated that static stretching (holding a stretch for a period) before exercise may not effectively reduce injury risk. In fact, some research shows that static stretching can temporarily weaken muscles, potentially leading to decreased performance, especially in sports requiring strength and power. Flexibility: A Double-Edged Sword While flexibility is important, excessive stretching can sometimes lead to hypermobility, which can be just as problematic as tightness. Hypermobile individuals may experience joint instability, increasing their risk of injury. Instead of focusing solely on stretching, a balanced approach that includes strength training and stability work may offer a more effective solution. The Case for Dynamic Movement Instead of traditional stretching, consider incorporating dynamic movements into your warm-up. Activities like leg swings, arm circles, and bodyweight exercises can effectively prepare your muscles for activity without the potential drawbacks of static stretching. Dynamic movements increase blood flow and activate muscles, leading to better performance without the risk of overstretching. If you are not sure what movement fit your needs, think about what exercises or sports acitiviy you are about to perform. An example would be a soccer match. Soccer involve running, quick change of direction, hip flexion and more lower body work. So what about doing some calf raises to warm up your calf muscles, which are going to be ready to make your run? Go for some squats that can focus on glute activation and quods activation, based on the type of squat that you are performing. Lunges that would ensure your quods warm up and your knees take some load. Plyometrics are a good way to warm up, too, such as skipping the rope or explosive squat. The Role of Massage and Other Therapies At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, we emphasize the benefits of massage therapy, myofascial release, and other treatments that promote muscle recovery and relaxation. These techniques can enhance flexibility and range of motion without the risks associated with excessive stretching. By addressing muscle tension and improving circulation, these therapies can provide a holistic approach to wellness. Tendons and Ligaments: The Stretching Sensitivity Tendons and ligaments are essential components of our musculoskeletal system, providing stability and support to our joints. Unlike muscles, which are designed to stretch and contract, tendons and ligaments are less pliable and don’t respond well to excessive stretching. When stretched beyond their natural limits, they can become overstressed, leading to micro tears or even injury. This lack of elasticity is why it’s crucial to approach flexibility with caution—overstretching can compromise the integrity of these structures, increasing the risk of strains and sprains. Instead of focusing on prolonged stretching, prioritizing strength and stability can help maintain healthy tendons and ligaments, ensuring that your body remains resilient and injury-free. What indeed our tendons and ligaments prefer as a form of activation are the isometric exercises. Conclusion While stretching may have its place, it’s crucial to question its effectiveness as a one-size-fits-all solution. Instead of defaulting to stretching, consider a more integrated approach that combines dynamic movement, strength training, and bodywork therapies. At Melbourne Massage and Treatment in Fitzroy North, we’re here to help you develop a personalized plan that prioritizes your health and well-being, and to start your journey book now a 15 minf free consultation for a treatment plan. Remember, wellness isn’t about following trends; it’s about finding what truly works for your body. Let’s move beyond the myths and embrace a more science-backed approach to fitness and recovery. FAQ Q: Why has stretching been considered important in fitness for so long? A: Stretching has been viewed as essential for improving flexibility, preventing injuries, and enhancing athletic performance, leading to its widespread adoption in pre- and post-workout routines. Q: Is there scientific evidence supporting the claim that stretching prevents injuries? A: Recent research indicates that static stretching before exercise may not effectively reduce injury risk. In fact, it can temporarily weaken muscles, potentially decreasing performance, especially in strength and power sports. Q: Can excessive stretching be harmful? A: Yes, excessive stretching can lead to hypermobility, which may cause joint instability and increase the risk of injury. A balanced approach that includes strength training is often more beneficial. Q: What are dynamic movements, and why are they preferred over static stretching? A: Dynamic movements, such as leg swings and arm circles, effectively prepare muscles for activity by increasing blood flow and activating muscles. They help improve performance without the drawbacks associated with static stretching. Q: How can I warm up effectively for specific sports? A: Tailor your warm-up to the activity. For example, before a soccer match, you might include calf raises, squats, and lunges to activate the necessary muscle groups and prepare your body for movement. Q: What role does massage therapy play in fitness and recovery? A: Massage therapy and myofascial release enhance muscle recovery and relaxation, improving flexibility and range of motion without the risks of excessive stretching. Q: How do tendons and ligaments respond to stretching? A: Tendons and ligaments are less pliable than muscles and can become overstressed when stretched excessively. This can lead to microtears or injury, making it important to approach flexibility with […]
Tendinopathy refers to the tendon’s painful or irritating condition, usually brought about by repetitive stress or overuse. Symptoms include pain, tenderness, and swelling in the affected area. It often results from activities that put excessive strain on the tendon or sudden increases in activity levels. What is a tendon? A tendon is a tough, flexible band of fibrous connective tissue that ties a muscle to a bone. The force generated by the muscle would be relayed through tendons onto the bones, thereby allowing movement of the body. Tendons are made of closely packed bundles of collagen fibers, which enable them to be strong enough to bear such stresses of activities. As tendons are not as stretchy as muscle fibres, they deal with load differently. Indeed, if put under an intense load, repetitively stretched, or used for repetitive movement, tendons get irritated. What are the stages of tendon degeneration? Regardless of age or biological gender, we will all experience some form of tendon degeneration throughout life. The more tendons are used, the earlier the degenerative process will be. In this context, we must reevaluate the negativity of the world’s “degeneration.” So, instead of giving a negative value to this world, let’s consider tendon degeneration only as a process of change in the tendon structure. This process is made of 3 stages: Reactive Tendinopathy: The first stage is characterized by a non-inflammatory reaction with a thickened tendon from increased protein production. The tendon can return to normal if the stress is reduced. Tendon Disrepair: If untreated, this is typically the second phase after reactive tendinopathy and is identified by further separation of collagen, disorganization of matrix, increased vascularity, and neural ingrowth. It normally needs to be diagnosed through imaging. Degenerative Tendinopathy: This is the final stage, characterized by permanent changes including cell death and marked matrix disorganization; it results in thickened and nodular tendons. Poor prognosis is associated with this condition. What to do when experiencing tendon pain? As you start experiencing pain, it is always suggested to reach out to a professional health therapist to evaluate what the problem is. In regards to tendon pain, the first step, independently from which stage of degeneration the tendon is in to, is suggested rest from the movement that flair up the area. On top of that the usage of heat pack is reccomended for a couple of times a day for 10 to 15 minutes. Tendon have a low blood supply compared to muscles, and the heat applied from outside can help in driving more blood to the area. Moving forward, if the pain is still present after three days, then the usage of an anti-inflammatory is recommended. The suggestion is to wait 3 days because, in the first three days of pain, the body puts in place what we call the “initial inflammatory response”, a phase in which the body increases blood volume to the area together with other biochemical reactions that kickstart the healing process. If, after three days, the inflammation has not ceased, that’s when the anti-inflammatories are needed. How do we treat tendinopathy at Melbourne Massage and Treatment? As a Clinical Myotherapist, I would suggest starting in the early stage with hands-on treatment and exercises-rehabilitation, such as a Myotherapy session. Past the first 3 days of inflammatory response, is good to start looking into why the presentation is not progressing for the better. Treatment modalities: Deep tissue massage is a modality that can stimulate relaxation and drive more blood to the area affected. Myofascial Dry Needling (MDN) can target the muscle attached to the tendon/s. It can help boost a new inflammatory response, desensitise the painful area, and increase muscle activation by interacting with the central nervous system. Exercises are then the takeaway for home. In the early stage, we would use isometric exercises to desensitize the area, partially load the muscle and keep the tendon active with constant load. This type of exercise can be used during the 1st or the 2nd week, based on the degenerative process we are dealing with. In terms of the time of load, based on the subjective finding, a time would be outlined. Roughly, we know that we are looking at an isometric load that would last about 30 to 45 secs with a break between one load and the next one, of the equivalent time. How long could it take to recover fully? Scientific studies have shown that the recovery process for tendinopathy varies from 3 weeks to 6 months. This is a big range of time, of course, and it is all about the gravity of the presentation, the tendon location, and the amount of rest that can be achieved along the recovery process. That said, as per all the exercises, the program is suggested for a minimum of three days a week and a maximum of five days a week. That would give enough time for the structure to be loaded and have time to recover, too. In conclusion, if you are suspicious of suffering from a tendinopathy, do not hesitate to reach out to Giovanni and Book Now for your next Myotherapy treatment. FAQ Q: What is tendinopathy? A: Tendinopathy is an injury to the tendons and results from repetitive stress or overuse. The result of the tendinopathy is pain, tenderness, and swelling into the affected area. Common activities causing this generally include over-straining or suddenly increasing the level of activity. Q: What is the degeneration process of the tendons? A: The tendon degeneration progresses in three stages: 1) Reactive Tendinopathy. 2) Tendon Disrepair. 3) Degenerative Tendinopathy. Q: What should I do if I have tendon pain? A: If suffering from tendon pain, basic things that you may try include: Rest the tendon from any activities that worsen the pain. Apply a heat pack for 10-15 minutes several times during the day as this helps to increase blood flow. Anti-inflammatory medication can be considered after three days, as this is typically when the initial inflammatory response has […]
Biomechanics is a branch of biophysics, and it studies the structure, function biomechanics is a branch of biophysics, and it studies the structure, function and motion of the mechanical aspects of biological systems using mechanical methods.d motion of the mechanical parts of biological systems using mechanical methods. Why is Body Biomechanics important? The way we move is a crucial component of injury prevention. Ensuring we are moving using our advantage, forces like gravity and body weight can help us reduce the chance of injury and improve the load capacity. To do so, we must train with a specific protocol that ensures excellent mobility to achieve muscular strength. What is a force? We can define a force as an influence that can change the motion of an object. Gravity is an acceleration that becomes a force when applied to a body. This concept was well explained by Netwon, with the announcement of Newton’s second law that can be summarised with F=m*a. F is the force, m is the mass, and a is acceleration. In the case of acceleration of gravity, it does measure 8.91 m/sec2. Said so, this means that we are constantly accelerated towards the ground. That’s why we don’t float in the air. And to better use this acceleration to our advantage, we have to move weight using the right angles. To better understand body biomechanics, we must introduce the idea of Moment Arm, Vector and Torque. What are Moment Arm Vector and Torque? And why are they essential for understanding human body biomechanics? The moment arm is the distance between the force and the joint that hold that force back. Think of yourself holding a water bottle up with your arm extended out. The joint holding up is your shoulder, the force is the combination of the bottle per the gravity a. (F=m*a). A Vector is the direction in which a force is applied. In this case, the direction is 90° downwards. Lastly, the Torque is the rapport between the Force and the Moment Arm. So, the shorter the moment arm, the easier it would be to lift an object. Understanding this concept would make your body biomechanics application much more accessible. Body biomechanics at the gym. When training at the gym, body biomechanics are fundamental. I often get clients in post-gym injury who don’t know much about mobility training, its importance, and body biomechanics. For example, keeping the weight so the bar is as close as possible to the leg is essential when doing a deadlift. This is because the weight has to be close to the Centre Of Gravity of the body, or the moment arm would be increased, so the torque required to lift the weight would increase too. In this case, the centre of gravity corresponds to the area where the actual torque is required, the lumbar area. Indeed, it is easy to hurt yourself on the lumbar when you bring that bar too far from your body. Body Biomechanic and Thai Massage Traditional Thai Massage, as offered at Melbourne Massage and treatment, tends to use the body biomechanics at its best. Even Thai Yoga exercises are based on the biomechanics principle, using lever and gravity as an advantage to create pressure on your body and reduce tension and heal aches. This, indeed, is what makes Traditional Thai Massage so unique. It is a technique of work where you don’t need great force, it is enough to use your body weight. And because it is delivered on a ground mat, it is easier to apply the biomechanics principles.
Tennis elbow or even known as Lateral Epicondylitis, is a condition that occurs on the lateral side of the forearm, at the elbow’s high. A common cause is repetitive motions of the wrist and arm. Tennis Elbow refers to how common this condition can be in tennis players. Said so, Lateral Epicondylitis is a condition that can affect anyone. As per Golfer’s Elbow, the pain starts from the elbow area, in this case from the lateral side, and can irradiate down the arm to the wrist. Rest and counter medication can help relieve symptoms. In some cases, surgery is required. Tennis Elbow Symptoms The pain generated by the tennis elbow may radiate down the forearm along the lateral side (thumb side). In addition to the pain, you may experience weakness too. Here is a list of actions that may be difficult to do Shake hands or grip an object Turn a door handle Hold a cup of water Book now your next appointment to restore the mobility of your Tennis Elbow Causes Tennis Elbow As Lateral Epicondolytis is overuse and strain of muscle, it is caused by repeated contraction of the forearm muscles extensor. These repetitive stretches and movements can lead to tiny tears in the tendon tissue, creating inflammation and pain within the elbow area. Playing tennis with the pour technique often replicates this condition, especially using repeated backhand strokes. Many other common motions can cause tennis elbow. Here is an extended list: Using plumbing tools, which require strong grips Painting Using screwdrivers Food preparation, especially when the knife is not sharp Working in the office using a mouse for long hours Treatment Options At Melbourne Massage and Treatment, Giovanni offers a variety of options for treating Lateral Epicondylitis. MLD may be the most recommended per inflammation of tendons and muscles. Thanks to the light touch and repetitive movement, MLD stimulates the Lymphatic System directly, which takes care of the inflamed area. Combining Myotherapy, Remedial Massage or Thai Massage technique with MLD can help even release more tension along the arm and elbow. Tennis Elbow Exercises In addition to the massage technique offered at Melbourne Massage and Treatment, exercises placed as per usual a crucial role in recovery. Specifically, we can look in too eccentric exercises, which slow, lengthening muscle contractions. Here is a link to eccentric exercises for the Tennis Elbow. As you may notice in this video, the extension motion of the wrist is supported by the other hand. By doing so, the extensor muscle of the forearm that needs training is not working hard. So the actual strengthening happens in the wrist’s flexion when the extensor muscles are stretching under the extra pressure of the weight.
Muscle and Tendon are two types of fibres that connect bonds, allowing the joint to be moved by contracting or extending. Muscles and Tendons characteristics. A muscle consists of fibres of muscle cells covered by fascia, bundled with many more fibres, surrounded by thick protective tissue. So each muscle fibre is covered in the fascia, then wrapped as a whole muscle in more fascia. A tendon is a high-tensile-strength band of dense fibery connective tissue. Indeed tendons can transmit the mechanical forces of muscle to the skeletal system. Tendons, as per ligaments, are made of collagen fibres. Compared to a tendon, a muscle is elastic and sits in between 2 tendons parts which keep the muscle itself connected to bonds. So yes, muscles are not directly connected to bond themself. Luckily, there is to say, because if this was the case, it would be really easy to suffer from injuries like a muscle tear. Said so, it is now easy to understand that tendons are capable of holding more force. Injury type Due to the consistency of the tendon and its functionality, we can now understand why a tendon tear or rupture is a severe injury that requires surgical intervention and months of rehabilitation. On the other hand, often, after months of rehabilitation, still, the tendon would not go back to its original state. A common tendon rupture is Achille’s tendon. Achille’s tendon connects the lower part of the Gastrocnemius and Soleus to the foothill. Repetitive movement and repetitive partial load on this tendon are the leading cause of injury. Healthy muscle and tendon Simple and gentle exercises are a good way to keep your muscle and tendon out of trouble. The key points of these types of exercises are: Consistency Resisted load (by using rubber bands) Starting with light weight to then building up with time heavier load Good posture doing the exercises Have a day of rest from exercises once a week Avoid exercises that aggravate your pain. Said so, other critical points for muscle and tendons good health seating into: Having a good night’s rest Eating more fresh food than overprocessed food Regarding recovery from an injury, as previously mentioned in the ice pack and/or heat pack posts, the usage of temperature is recommended based on the stage of the injury and the pain experienced with it. Even though on an inflamed tendon, never apply a heat pack. Are you in need of treatment? Don’t look any further, and book your initial consultation by clicking here.